Important Facts of the News
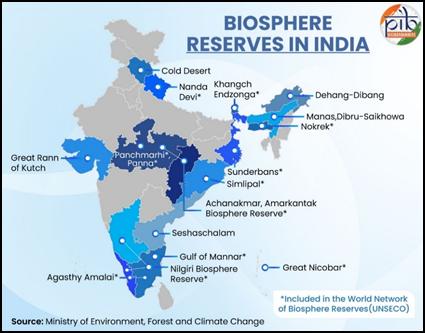
- India has 18 Biosphere Reserves covering 91,425 sq. km.
- Out of these, 13 are part of UNESCO’s World Network of Biosphere Reserves.
- India ranks 9th globally in total forest area and 3rd in annual forest gain (FAO, 2025).
- The funding pattern for Biosphere Reserves is 60:40 (Centre: State), and 90:10 for North Eastern and Himalayan regions.
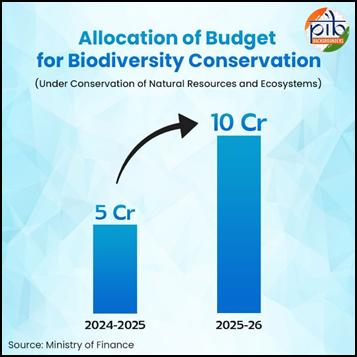
- The conservation budget increased from ₹5 crore in 2024-25 to ₹10 crore in 2025-26.
- Cold Desert Biosphere Reserve, Himachal Pradesh, was added to UNESCO’s list in 2025.
- Over 260 million people live within biosphere reserves globally.
- Biosphere Reserves protect more than 7 million sq. km worldwide.
- India’s biosphere reserves integrate biodiversity conservation with local community welfare.
- Programmes like Project Tiger and Project Elephant support biosphere reserve goals.
Celebrating International Biosphere Reserves Day
Every year on November 3, nations worldwide commemorate the International Day for Biosphere Reserves. This observance highlights regions where people coexist harmoniously with nature. India joins this global initiative by showcasing its active network of biosphere reserves that span mountains, forests, islands, and coastlines.
These reserves, recognized locally and globally, serve as experimental platforms for sustainable living. They demonstrate real-world solutions for conserving biodiversity while ensuring livelihoods for surrounding communities.
Understanding India’s Biosphere Reserves
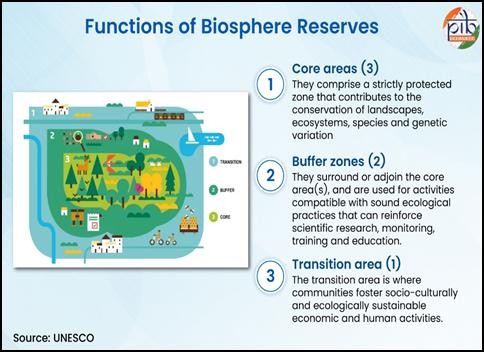
Biosphere reserves are defined areas where environmental protection goes hand in hand with sustainable development. In India, 18 such regions have been formally designated and serve as models for balancing human needs with natural ecosystems.
Among them, 13 reserves, including well-known regions like Nilgiri, Sundarbans, and Nanda Devi, have attained recognition under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme.
UNESCO’s Role and Global Perspective
Under the MAB Programme, UNESCO facilitates international cooperation by designating biosphere reserves that reflect a diverse range of ecosystems. These learning sites promote harmony between people and nature, placing equal emphasis on cultural values and scientific advancement.
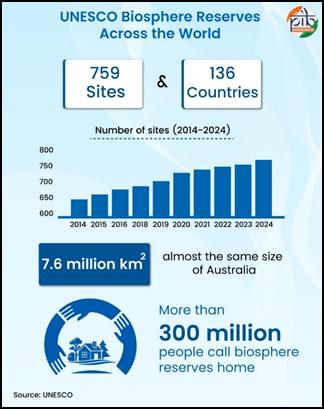
Globally, more than 260 million people live within biosphere reserves, which collectively protect over 7 million sq. km of land and sea.
India’s Efforts and Achievements
India’s Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) oversees a centrally sponsored scheme supporting these reserves. The government contributes 60 percent of the funding for most states and 90 percent for North Eastern and Himalayan states.
The recent budget doubled the allocation for biodiversity conservation from ₹5 crore in 2024-25 to ₹10 crore in 2025-26, enabling enhanced conservation measures and livelihood support for local communities.
India’s rising global position in forest management is reflected in the FAO’s 2025 findings: the country ranks 9th in forest area and 3rd in annual increase, thanks in part to its comprehensive conservation approach.
Complementary National Initiatives
National schemes like Project Tiger and Project Elephant reinforce biosphere reserve missions. Other goals are met through the Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats (IDWH), National Biodiversity Action Plan (NBAP), and the Green India Mission.
These programmes, when combined with biosphere reserve strategies, foster ecological balance, strengthen habitats, and uplift local communities through participatory conservation.
Conclusion
India’s biosphere reserves are a testament to its commitment to conservation and sustainability. Beyond preserving ecology, these reserves nurture harmonious communities and reinforce India’s standing as a global leader in sustainable development. Through collaborative efforts and forward-looking policies, India strengthens the bond between people and nature, ensuring a living legacy for generations ahead.